 Embedding alignement pipeline
Embedding alignement pipelineAbstract
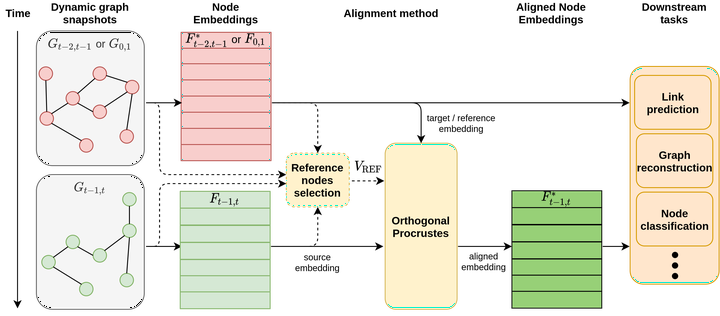
In recent years, dynamic graph embedding has attracted a lot of attention due to its usefulness in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we consider discrete-time dynamic graph representation learning, where embeddings are computed for each time window, and then are aggregated to represent the dynamics of a graph. However, independently computed embeddings in consecutive windows suffer from the stochastic nature of representation learning algorithms and are algebraically incomparable. We underline the need for embedding alignment process and provide nine alignment techniques evaluated on real-world datasets in link prediction and graph reconstruction tasks. Our experiments show that alignment of Node2vec embeddings improves the performance of downstream tasks up to 11 pp compared to the not aligned scenario.